The United States of America
See the vocabulary here:
Table Of Contents
Table Of Contents
- The United States of America
- See the vocabulary here:
- Geographical facts about The USA
- US States:
- The History of The USA
- 1. Indigenous Civilizations (Before 1492)
- 2. European Colonization (1492–1776)
- 3. The American Revolution (1775–1783)
- 4. The Formation of the USA (1787–1800s)
- 5. The Civil War and Reconstruction (1861–1877)
- 6. Industrialization and Expansion (Late 1800s–Early 1900s)
- 7. World Wars and the Great Depression (1914–1945)
- 8. The Cold War and Civil Rights (1945–1991)
- 9. The Modern USA (1991–Present)
- The Political System
- See the summarising video
- Good luck with Maturita!
Geographical facts about The USA
General Information
- Official Name: United States of America (USA)
- Continent: North America
- Total Area: ~9.8 million km² (3.8 million mi²)
- Population: ~332 million (as of recent estimates)
- Capital City: Washington, D.C.
- Largest City: New York City
- Official Language: No official language at the federal level, but English is the de facto language
- Currency: US Dollar (USD)
Borders and Location
- Neighbouring Countries:
- Canada (north)
- Mexico (south)
- Coastlines:
- Atlantic Ocean (east)
- Pacific Ocean (west)
- Gulf of Mexico (southeast)
Geographical Features
- Highest Point: Mount McKinley – 6,190 m (20,310 ft)
- Lowest Point: Badwater Basin, Death Valley – -86 m (-282 ft)
- Longest River: Missouri River (~3,767 km / 2,341 mi)
- Largest Lake: Lake Superior (~82,100 km² / 31,700 mi²)
Climate and Regions
- Major Climate Zones:
- Temperate (most of the country)
- Tropical (Florida, Hawaii)
- Desert (Southwest)
- Arctic (Alaska)
- Main Geographical Regions:
- The West (mountains, deserts, Pacific coast)
- The Midwest (plains, Great Lakes)
- The South (humid, subtropical, Gulf coast)
- The Northeast (forests, coastal areas, Appalachian Mountains)
Natural Disasters and Hazards
- Common Natural Disasters: Hurricanes, tornadoes, wildfires, earthquakes
- Tornado Alley: Central USA (Kansas, Oklahoma, Texas, Nebraska)
- Earthquake-prone Areas: West Coast (California, Alaska)
Political Divisions
- Number of States: 50
- Largest State (by area): Alaska
- Smallest State (by area): Rhode Island
Largest & Most Influential Cities
- New York City, NY – Largest city, financial and cultural hub
- Los Angeles, CA – Entertainment and tech industry
- Chicago, IL – Business, architecture, transportation hub
- Houston, TX – Energy, space, and medical research
- Phoenix, AZ – Fast-growing city, desert climate
- Philadelphia, PA – Historic significance, education
- San Antonio, TX – Military, tourism (Alamo)
- San Diego, CA – Naval base, biotech, beaches
- Dallas, TX – Business, tech, oil industry
- San Jose, CA – Center of Silicon Valley (tech hub)
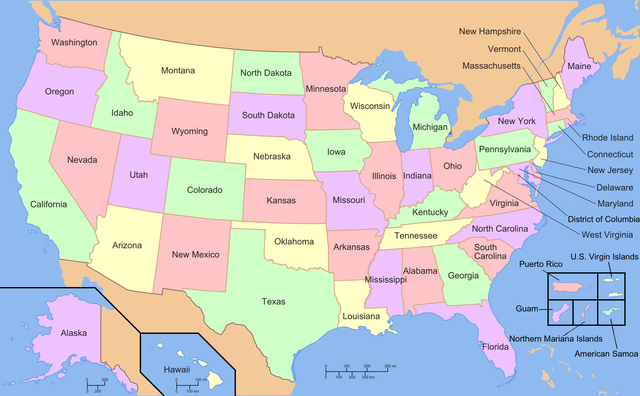
US States:
The History of The USA
1. Indigenous Civilizations (Before 1492)
Before European arrival, North America was home to many indigenous nations, including the Cherokee, Iroquois, Sioux, and Apache. These societies had rich cultures, complex political systems, and trade networks.
2. European Colonization (1492–1776)
- 1492: Christopher Columbus arrived in the Americas, initiating European colonization.
- 1607: The first permanent English settlement, Jamestown, was founded in Virginia.
- 1620: The Pilgrims landed at Plymouth, seeking religious freedom.
- The 17th and 18th centuries saw the expansion of British, French, and Spanish colonies, the transatlantic slave trade, and conflicts with indigenous peoples.
3. The American Revolution (1775–1783)
- Boston Tea Party (1773): Colonial protest against British taxes. Disguised colonists dumped British tea into Boston Harbor. Britain retaliated with harsh laws, fueling the American Revolution.
- 1775: The Revolutionary War began between the 13 American colonies and Britain.
- 1776: The Declaration of Independence, written by Thomas Jefferson, was adopted on July 4.
- 1783: The war ended with the Treaty of Paris, and Britain recognized American independence.
4. The Formation of the USA (1787–1800s)
- 1787: The U.S. Constitution was drafted, establishing a democratic government.
- 1789: George Washington became the first president.
- The Bill of Rights (1791) guaranteed civil liberties.
- The USA expanded westward, purchasing Louisiana from France (1803) and displacing Native American tribes.
5. The Civil War and Reconstruction (1861–1877)
- 1861: The Civil War erupted between the North (Union) and the South (Confederacy) over slavery and states’ rights.
- 1863: Abraham Lincoln issued the Emancipation Proclamation, freeing enslaved people in rebel states.
- 1865: The war ended, slavery was abolished (13th Amendment), and Lincoln was assassinated.
- Reconstruction (1865–1877): The South was rebuilt, but racial tensions persisted.
6. Industrialization and Expansion (Late 1800s–Early 1900s)
- The USA became an economic and industrial power.
- Millions of immigrants arrived, mostly from Europe.
- Native American lands were taken, and conflicts, like the Battle of Little Bighorn (1876), occurred.
7. World Wars and the Great Depression (1914–1945)
- World War I (1917–1918): The USA joined the Allies, helping to defeat Germany.
- The Great Depression (1929–1939): The stock market crash led to economic collapse.
- World War II (1941–1945): After Japan attacked Pearl Harbor, the USA joined the war, helping the Allies win.
- The war ended with atomic bombings of Hiroshima and Nagasaki (1945).
8. The Cold War and Civil Rights (1945–1991)
- The USA and the Soviet Union entered the Cold War, competing in nuclear arms, space exploration (NASA, Moon landing in 1969), and ideology.
- The Civil Rights Movement (1950s–1960s) fought racial segregation, led by Martin Luther King Jr.
- Vietnam War (1955–1975): A controversial war against communism.
9. The Modern USA (1991–Present)
- 1991: The Cold War ended as the Soviet Union collapsed.
- 2001: 9/11 terrorist attacks led to the War on Terror (Afghanistan, Iraq).
- 2008: Barack Obama became the first African American president.
- Recent issues include political polarization, climate change, and global leadership in technology and culture.
The Political System

Donald J. Trump
The 47th President of The United States of America
Type of Government
- Federal presidential constitutional republic
- Power is divided between federal and state governments
- Operates under the US Constitution
Separation of Powers
- Legislative Branch (Congress) – Makes laws
- Executive Branch (President) – Enforces laws
- Judicial Branch (Supreme Court & Federal Courts) – Interprets laws
- Checks and balances prevent abuse of power
Legislative Branch (Congress)
- Bicameral (two chambers):
- Senate – 100 members (2 per state, 6-year terms)
- House of Representatives – 435 members (based on population, 2-year terms)
- Powers: Makes laws, approves budgets, declares war
Executive Branch (President & Administration)
- President: Head of state, head of government, commander-in-chief
- Elected for 4 years (max. 2 terms)
- Can veto laws, appoint judges, negotiate treaties
Judicial Branch (Supreme Court & Federal Courts)
- Supreme Court – Highest court (9 justices, appointed for life)
- Reviews laws and government actions for constitutionality
Federal System
- Power is shared between federal and 50 state governments
- States have their own governors, legislatures, and courts
- State laws must follow the US Constitution
Political Parties
- Two-party system:
- Democratic Party (liberal, left-leaning)
- Republican Party (conservative, right-leaning)
- Third parties exist but are less influential
Elections & Voting
- Presidential elections – Every 4 years (via Electoral College)
- Congressional elections – Every 2 years
- Voting age: 18+ (citizens only)
See the summarising video
Good luck with Maturita!
(Created with a help of ChatGPT and Revisely)
